Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
-->
Mining Influencers in the German Twittersphere: Mapping a Language-Based Follow Network (IC2S2 2019)
Thu, 10/10/2019 - 15:05 — SnurbIC2S2 2019 [9]
Mining Influencers in the German Twittersphere: Mapping a Language-Based Follow Network
Felix Victor Münch, Ben Thies, Cornelius Puschmann, and Axel Bruns
- 18 July 2019 – International Conference on Computational Social Science [9], Amsterdam
Mining Influencers in the German Twittersphere – Mapping a Language-Based Follow Network [10]from Felix Victor Münch [11]
Extended Abstract
This conference contribution presents a new sampling approach for large follow networks of influential Twitter accounts, discusses first key results of its application to the German Twittersphere, and benchmarks their representativeness.
Twitter plays a major role in public communication as a preferred medium for politicians, journalists, and celebrities to directly communicate with their audiences. The structures and dynamics on the platform stand exemplarily as a source of empirical evidence for recent theories about a networked public sphere (Bruns, 2008; Bruns & Highfield, 2016). Not only is it possible to identify characteristic communication structures regarding specific topics, such as polarised crowds or community clusters (Himelboim, Smith, Rainie, Shneiderman, & Espina, 2017), but also to investigate the macro-structures of whole national Twitterspheres, for example, of Australia (Bruns, Moon, Münch, & Sadkowsky, 2017) and Norway (Bruns & Enli, 2018). However, for Germany, a similar overview of a national Twittersphere is missing, which hinders the examination of such phenomena within a German context. This is mainly due to the restrictive access policies of Twitter and its data vendors that make the gathering of a comprehensive dataset, as has been done for the Australian and Norwegian cases, a costly and/or time-consuming task.
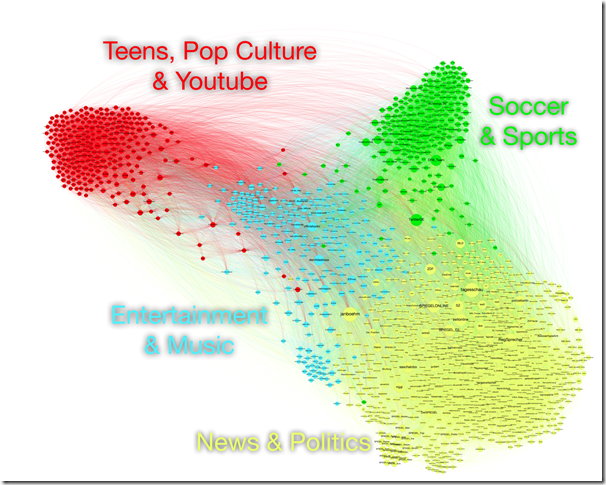
Therefore, this ongoing project tests a new sampling approach to generate a large sample of the follow network of the most influential accounts in the German Twittersphere. Instead of collecting the follow connections of all German-speaking Twitter accounts, the data collection process used in this project is based on an adaption of the rank degree method (Salamanos, Voudigari, & Yannakoudakis, 2017b). This graph sparsification method has been shown to facilitate the identification of the most influential nodes in epidemic network models with samples of only small subgraphs of the full network, while preserving characteristic network measures (Salamanos, Voudigari, & Yannakoudakis, 2017a). The algorithm, in short, crawls the network by following paths through nodes with the highest degree. As it only needs locally available information on the network structure, we have adapted and implemented it to drive a data mining approach using Twitter’s standard Search API. So far, we have collected a network sample of over 800,000 nodes (Figure 1). The collection is still ongoing and aims for a sample of one million nodes. To test the representativeness of the sample, this project compares these new sample data against an existing dataset that has been collected by Bruns et al. (2017), comprising account details of all publicly accessible Twitter accounts in 2016.
Figure 1. Directed follow network of most influential Twitter accounts (1,481 nodes, 99,442 edges, comprising the giant component of the k-core with k = 50, excluding two identified bot-nets with 399 accounts total) from our German sample (839,049 nodes, 1,442,552 edges at time of writing); coloured by groups determined with modularity maximization, size of nodes corresponds with page rank, edges are coloured like their source node.
This project provides a first authoritative representation of the German Twittersphere which enables further research, reveals community structures of influencers in the German Twittersphere, and permits inferences about changes in follow behaviours after recommendation algorithms were introduced on Twitter. Furthermore, the tested collection approach, whose code will be published under an open source license, will enable researchers to easily collect follow network samples of other countries’ public spheres, based on languages and time zones, as well as around arbitrary Twitter accounts of interest.
References
Bruns, A. (2008). Life beyond the public sphere: towards a networked model for political deliberation. Information Polity, 13, 71–85.
Bruns, A., & Highfield, T. (2016). Is Habermas on Twitter? Social Media and the Public Sphere. In The Routledge Companion to Social Media and Politics (pp. 56–73). Retrieved from https://eprints.qut.edu.au/91810/ [13]
Bruns, A., Moon, B., Münch, F. V., & Sadkowsky, T. (2017). The Australian Twittersphere in 2016: Mapping the Follower/Followee Network. Social Media + Society, 3(4). http://doi.org/10.1177/2056305117748162 [14]
Bruns, A., & Enli, G. (2018). The Norwegian Twittersphere: Structure and Dynamics. Nordicom Review, 1–20. http://doi.org/10.2478/nor-2018-0006.1 [15]
Himelboim, I., Smith, M. A., Rainie, L., Shneiderman, B., & Espina, C. (2017). Classifying Twitter Topic-Networks Using Social Network Analysis, 1–38. http://doi.org/10.1177/2056305117691545 [16]
Salamanos, N., Voudigari, E., & Yannakoudakis, E. J. (2017a). A graph exploration method for identifying influential spreaders in complex networks. Applied Network Science, 2(1), 26. http://doi.org/10.1007/s41109-017-0047-y [17]
Salamanos, N., Voudigari, E., & Yannakoudakis, E. J. (2017b). Deterministic graph exploration for efficient graph sampling. Social Network Analysis and Mining, 7(1), 24. http://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-017-0441-6 [18]
![Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.0 License [Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.0 License]](http://creativecommons.org/images/public/somerights20.gif)